2024-05-21
Creating a Safe and Fun Outdoor Learning Space
Outdoor play is essential to a child’s development, providing unique opportunities not typically found in an indoor space. An engaging outdoor environment offers a child a blend of play and learning, where children can explore, discover, and grow. The natural world becomes a dynamic classroom where outdoor activities foster physical, cognitive, and emotional growth.
Creating an effective outdoor learning environment involves more than just providing a space for children to play. It requires thoughtful design and incorporating various elements that support different aspects of development. From activity panels and sensory gardens to simple setups like a picnic table for collaborative projects, each component enhances the outdoor learning space and experience. Outdoor activities benefit physical health and stimulate cognitive development and social skills, making them indispensable in a well-rounded educational approach.
This article will explore the numerous benefits of outdoor play and provide practical tips for creating engaging outdoor spaces that support child development. Educators and parents can create enriching environments that encourage children to explore, learn, and thrive by integrating a fun activity with various educational elements and ensuring safety.


Benefits of an Outdoor Learning Environment
Learning outdoors offers numerous advantages for young children, enhancing their development across multiple domains. Physically, outdoor play encourages children to be active, helping to improve their gross motor skills and overall physical health. Engaging in running, climbing, and jumping supports muscle development and coordination, which are critical for their growth.
Key benefits to learning outdoors:
- Physical Development: Enhances gross motor skills and physical health through active play.
- Cognitive Development: Stimulates problem-solving and cognitive abilities through interactive and exploratory activities.
- Emotional and Social Development: Promotes emotional well-being and social skills through cooperative play and interaction.
- Connection with Nature: Encourages appreciation and understanding of nature through hands-on exploration.
Outdoor spaces also play a significant role in cognitive development. When children interact with nature, they engage in hands-on learning activities, stimulating their curiosity and creativity. Exploring natural materials, observing wildlife, and participating in structured educational activities like scavenger hunts help develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This learning environment supports various aspects of cognitive growth, including memory, attention, and language skills.
Emotionally and socially, an outdoor environment provides a unique setting for children to develop essential social skills. Playing in groups allows children to practice cooperation, negotiation, and conflict resolution. The open, less structured nature of outdoor play also gives children the freedom to express themselves, which can be particularly beneficial for their emotional well-being. Being in a natural setting has a calming effect, reducing stress and anxiety and improving overall mental health.
Lastly, connecting with nature fosters a sense of appreciation and responsibility toward the environment. Learning outdoors encourages children to observe and interact with nature, which can lead to a lifelong interest in environmental stewardship. Activities such as planting gardens, observing insects with magnifying glasses, and learning about local ecosystems help children develop a deeper understanding and respect for nature. This connection enhances their learning and improves their emotional and social development by fostering a sense of belonging and purpose.


Designing Safe and Engaging Outdoor Spaces
Creating a safe and engaging outdoor space is essential for maximizing the benefits of outdoor play. When designing outdoor environments, it’s important to consider safety, using organic materials, and selecting durable equipment. Ensuring these elements are in place helps create a space where children can explore, learn, and play freely without unnecessary risks.
Safety is the top priority in any outdoor play space. This involves choosing equipment that meets safety standards, regularly inspecting the play area for hazards, and ensuring that surfaces are designed to prevent injuries. Using organic materials enhances the play space’s aesthetic appeal and encourages children to engage more deeply with their surroundings. Durable equipment ensures the play space remains functional and safe over time, even with frequent use.
Safety Considerations
Designing an outdoor play area begins with a focus on safety. All play equipment should meet current safety standards and be regularly inspected for wear and tear. Surfaces should be soft and impact-absorbing, such as rubber mulch or grass, to minimize injuries from falls. It’s also crucial to provide clear sightlines for supervision and ensure the play area is free from hazards like sharp objects or toxic plants. Incorporating safe pathways and adequate lighting can further enhance the safety of the space, allowing children to explore confidently.
Use of Natural Materials and Durable Equipment
Incorporating natural and organic materials into the design of learning outdoors enriches children’s play experiences by connecting them to nature. Elements like wood, sand, and plants provide sensory stimulation and opportunities for creative play. Durable play equipment, made from high-quality materials like treated wood and weather-resistant metals, ensures that the play area can withstand the elements and heavy use. These materials enhance the play structures’ longevity and create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly play space.
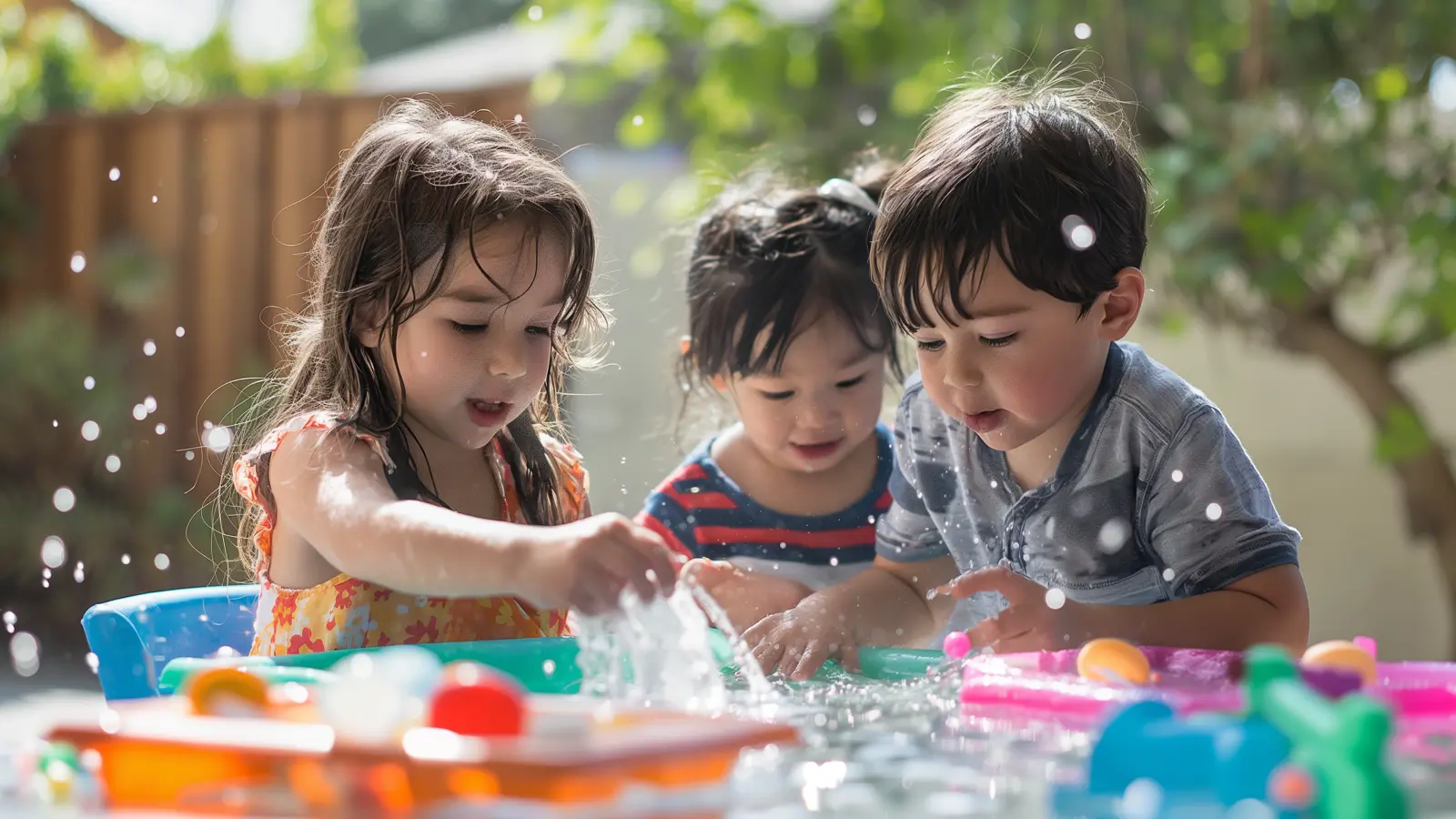


Integrating Educational Elements into Play Spaces
Integrating educational elements into outdoor play spaces significantly enhances children’s learning experiences. These elements should be thoughtfully selected to support various aspects of development, including cognitive, sensory, and motor skills. By incorporating educational tools into dramatic play, such as activity panels, sensory gardens, and interactive play elements, learning in an outdoor environment becomes vibrant and encourages exploration and discovery.
Activity panels are a fantastic way to integrate learning directly into your children’s play. These panels can include puzzles, counting games, and other educational activities challenging children’s cognitive abilities. For example, a panel with shapes and colors can help young children develop their understanding of basic concepts while also enhancing their fine motor skills as they manipulate the pieces. Additionally, these panels encourage social interaction as children work together to solve problems or share their discoveries.
Educational elements you can add:
- Activity Panels: Include puzzles, counting games, and educational activities.
- Sensory Gardens: Engage children’s senses and provide hands-on learning opportunities.
- Interactive Play Elements: Water tables and loose parts for creative exploration.
- Natural Materials: Integrate wood, sand and plants to enrich sensory experiences.
Sensory gardens are another excellent educational tool for learning outdoors. These gardens are designed to engage children’s senses through various plants and materials they can touch, smell, see, and sometimes even taste. Sensory gardens can include a mix of flowers, herbs, and textured plants that provide different sensory experiences. These gardens help children learn about nature and promote relaxation and emotional well-being. Sensory play also supports cognitive development by encouraging children to observe, question, and explore their surroundings.
Interactive play elements like water tables and loose parts foster creativity and problem-solving skills. A water table, for instance, allows children to experiment with the properties of water, learning concepts such as buoyancy and volume through hands-on play. Loose parts, such as stones, sticks, and leaves, can be used in countless ways, sparking children’s imagination and creativity. These elements support open-ended play, where children can explore and create based on their interests and ideas, promoting deeper engagement and learning.
Using organic materials in outdoor play spaces enhances sensory experiences and connects children to the environment. Incorporating wood, sand, and plants into the play area encourages children to explore and interact with nature. This connection is essential for fostering a sense of environmental stewardship and appreciation. Natural and organic materials also provide varied textures and sensory inputs that benefit children’s development, helping them build a more profound connection with their surroundings and supporting holistic growth.
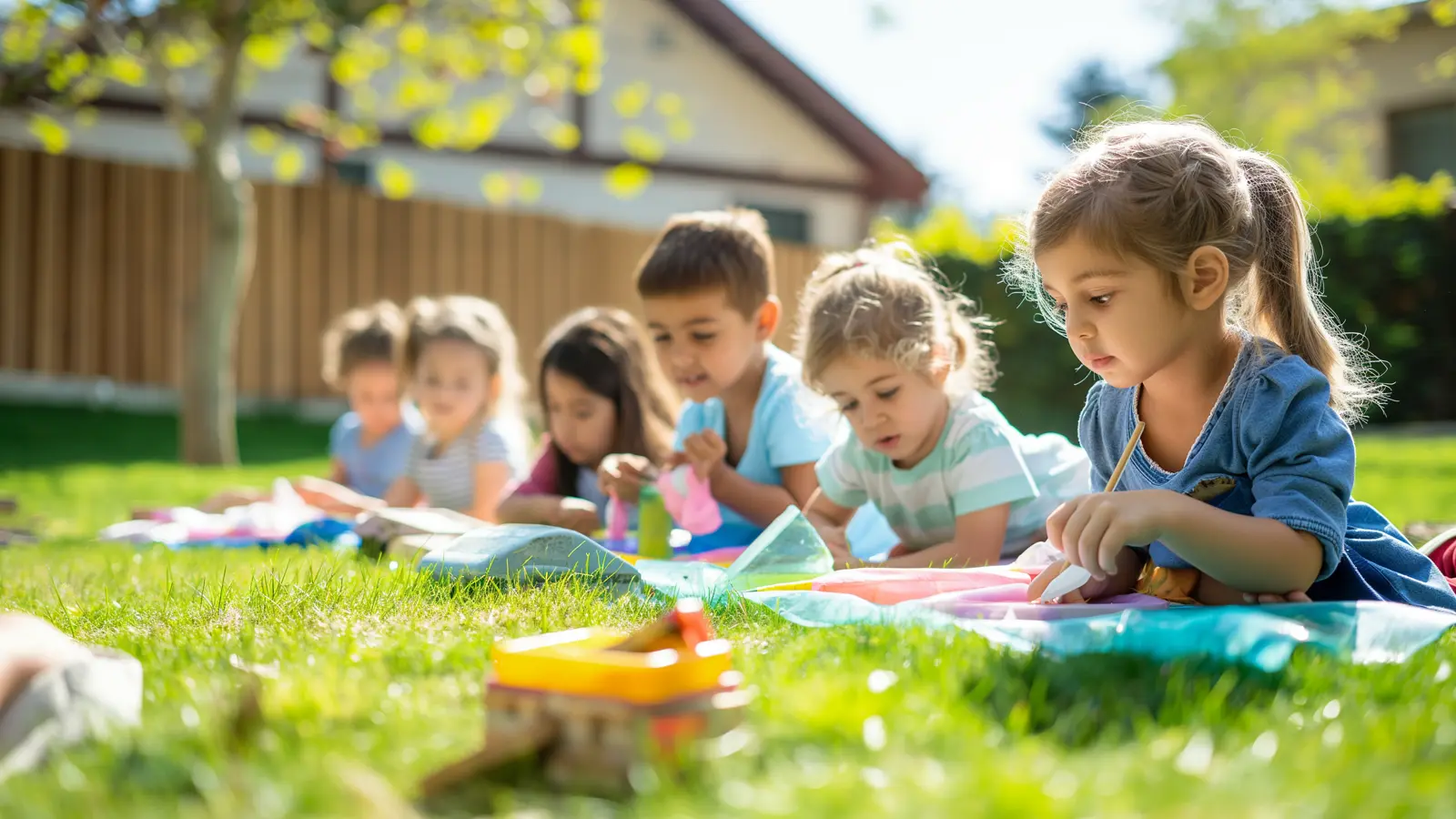


Encouraging Exploration and Discovery
Encouraging exploration and discovery in learning outdoors is vital to fostering children’s natural curiosity and love for learning. Outdoor environments provide numerous opportunities for children to engage with nature, promoting cognitive and sensory development. Educators can create rich, engaging experiences that enhance children’s understanding and appreciation of their surroundings by providing tools and activities that support exploration.
Outdoor spaces that encourage exploration often include various tools and materials that invite children to investigate and learn. Bird feeders and water tables are just some items that can spark curiosity and promote hands-on learning. These tools help children observe and interact with their environment, leading to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of nature. Such experiences are essential for developing problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and a sense of wonder about the world around them.
Nature Exploration Tools
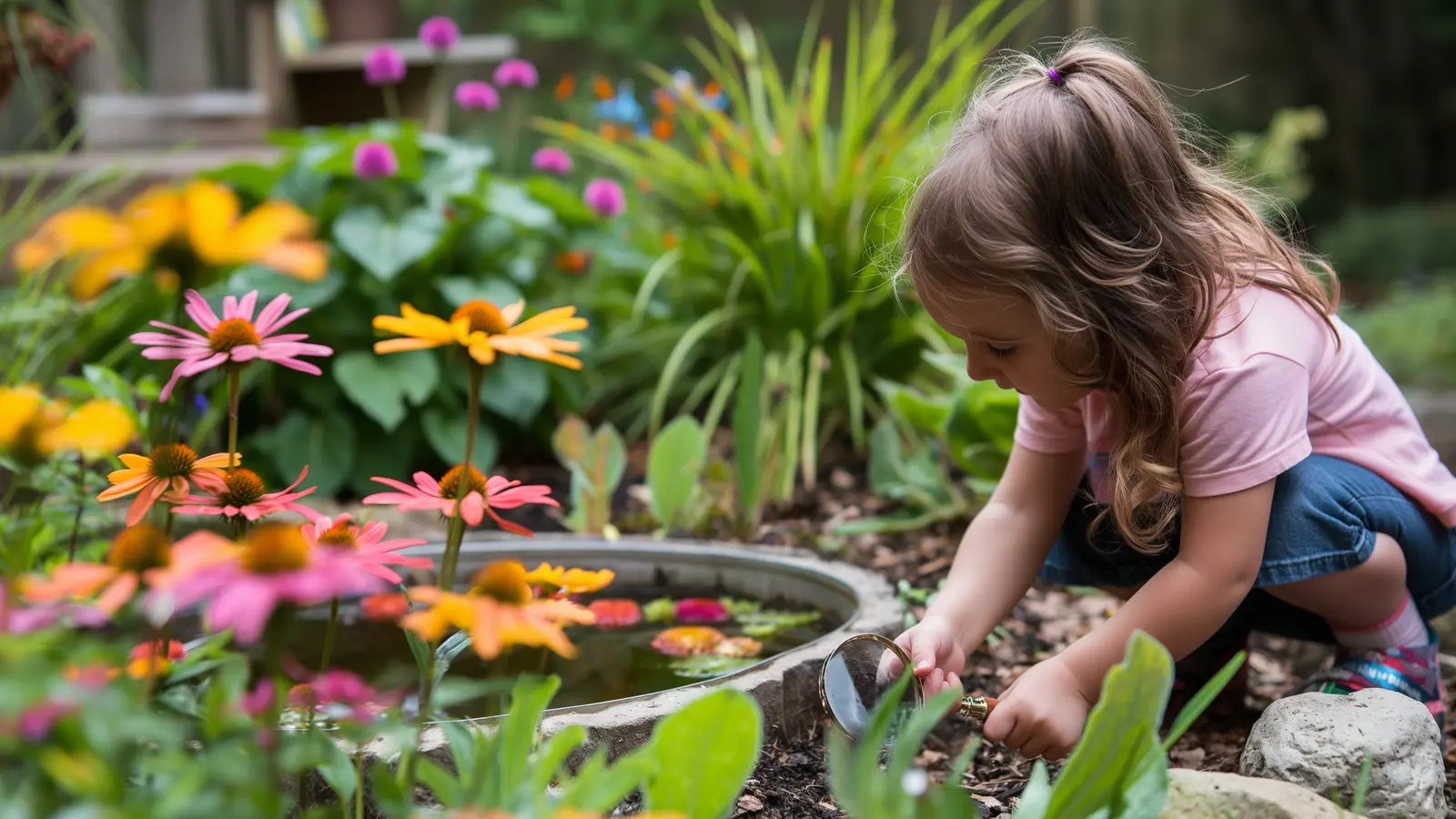
Providing tools like magnifying glasses, binoculars, and bug jars allows children to observe plants, insects, and other natural elements closely. This hands-on approach encourages detailed observation and inquiry, helping children develop scientific thinking skills. For instance, magnifying glasses to examine leaves or insects can lead to discussions about different species and their habitats, promoting a deeper connection to the natural environment.
Wildlife Study
Setting up bird feeders and baths in the play area can attract various bird species, allowing children to learn about local wildlife. Observing birds and other animals helps children develop patience and observation skills. Educators can enhance this experience by incorporating bird identification guides into lesson plans and encouraging children to journal their observations, fostering a sense of responsibility and interest in wildlife conservation.
Sensory Play
Incorporating sensory play elements such as water tables and sandboxes offers children valuable sensory experiences. These activities allow children to explore textures, temperatures, and the properties of different materials, enhancing their sensory development. Water tables, for instance, can be used to explore concepts like buoyancy and water flow, while sandboxes can encourage digging and building, supporting fine motor skills and creative expression.
Educators can thoughtfully incorporate these elements into outdoor learning environments to create spaces that support exploration and discovery and promote holistic development. These activities encourage children to engage with their surroundings meaningfully, fostering a lifelong love of learning and a deep connection to nature.


Promoting Physical and Cognitive Development
Outdoor play is essential for the holistic development of young children, particularly in promoting physical and cognitive growth. Children engaging in outdoor activities naturally develop gross motor skills through running, jumping, climbing, and other physical movements. These activities support overall physical health and are crucial for children’s play and development.
The benefits of outdoor play extend beyond physical development to cognitive growth. Engaging in outdoor activities encourages children to think critically, solve problems, and explore their environment. Activities such as building with loose parts, participating in obstacle courses, and imaginative play in outdoor spaces cognitively stimulate creativity. Additionally, these activities provide opportunities for young children to develop language skills as they communicate and collaborate with peers.
Skills children learn through outdoor learning activities:
- Gross Motor Skills: Enhanced through running, climbing, and jumping.
- Problem-Solving: Encouraged by building with loose parts and obstacle courses.
- Language Development: Fostered through communication and collaboration in play.
- Cognitive Skills: Stimulated by imaginative play and exploration.
The outdoors offers unique opportunities for physical activity that indoor spaces cannot replicate. Children can run freely, navigate uneven terrain, and engage in more vigorous play, which is vital for developing strong muscles and coordination. These experiences also help younger children learn about their physical capabilities and limitations in a safe and supportive setting. By providing diverse outdoor learning areas, educators can ensure that children have ample opportunities to be physically active and develop essential motor skills.
Engaging in an outdoor learning activity allows children to express themselves freely and manage their emotions. Nature offers a calming effect, helping to reduce stress and anxiety. Children who play outdoors experience a sense of freedom and independence, crucial for building self-confidence and resilience. Outdoor areas that include quiet spaces for reflection and active play areas provide a balanced environment that caters to children’s emotional needs.
Furthermore, playing outdoors fosters social skills and teamwork as children interact with their peers. Group activities, such as building a fort or playing a team game, require cooperation, negotiation, and shared decision-making. These interactions help children learn to work together, understand different perspectives, and develop empathy. The social aspect of outdoor play is vital for children’s well-being and helps prepare them for future social interactions and relationships.


Fostering Social Skills and Emotional Growth
Outdoor play significantly contributes to children’s social and emotional development. In outdoor environments, children can interact with their peers in more dynamic and less structured ways than in indoor spaces. These interactions are crucial for developing social skills such as cooperation, negotiation, and conflict resolution. The freedom and space provided by outdoor settings encourage children to engage in group activities and collaborative play, which are essential for their social growth.
Outdoor spaces also play a vital role in supporting emotional development. Being in nature has a calming effect on children, helping to reduce stress and anxiety. Outdoor activities provide a sense of freedom and autonomy, allowing children to express their emotions openly and manage their feelings in a safe environment. Activities like exploring nature, engaging in imaginative play, and participating in physical activities can significantly enhance children’s emotional well-being and resilience.
Combining physical activity and outdoor play further supports emotional and social development by fostering a sense of accomplishment and self-confidence. When children successfully navigate an obstacle course or a challenging play structure or cooperate to achieve a common goal, they build confidence in their abilities and learn to trust themselves and others. This boost in self-esteem is critical for their overall emotional health and social competence.
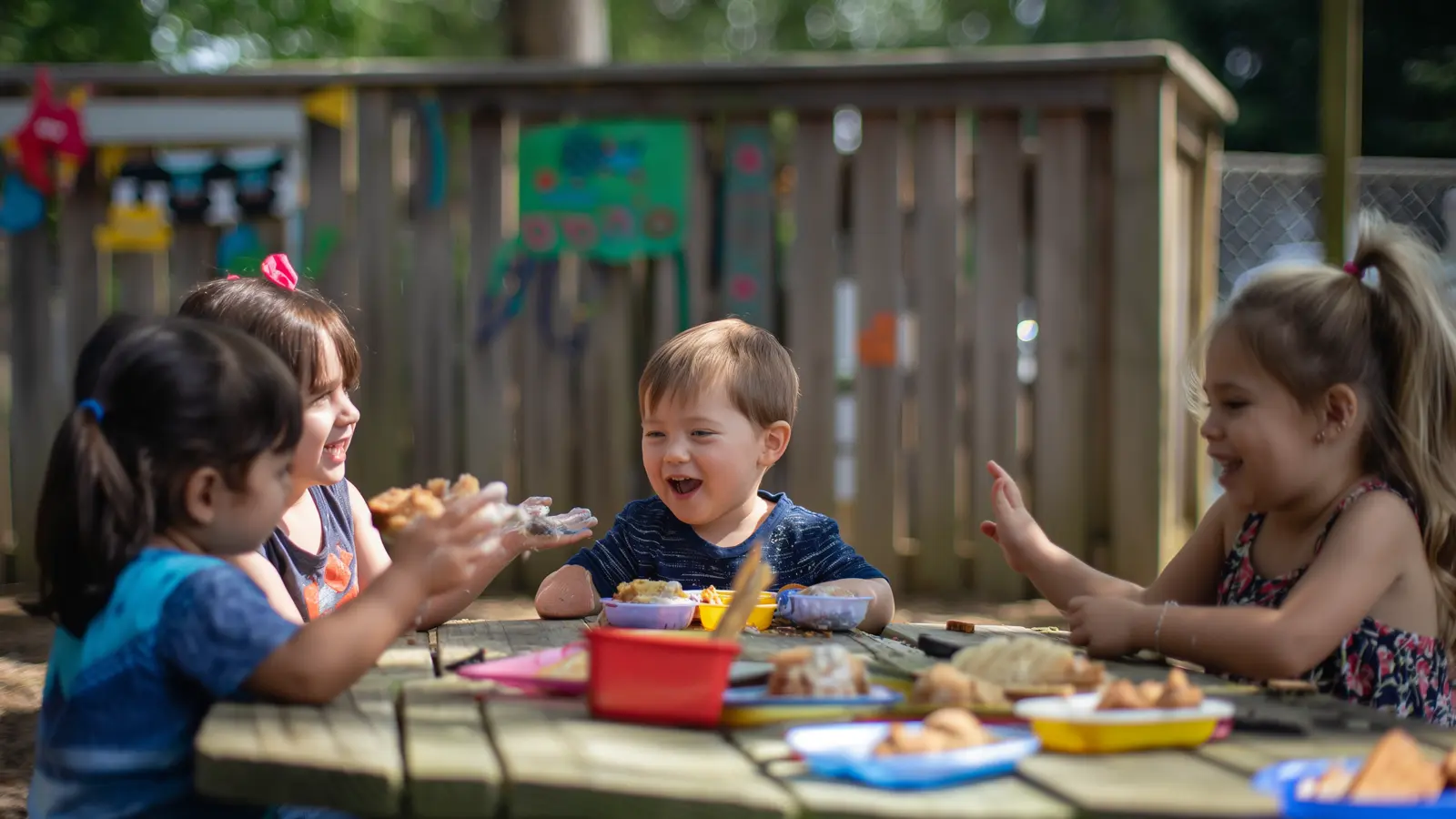
Group Activities
Group activities in outdoor learning environments encourage children to work together, share ideas, and support each other. Picnic tables, for example, can be used for collaborative art projects, group discussions, and shared meals, promoting a sense of community and cooperation. These activities help preschool children develop essential social skills, communicate effectively, and understand the value of teamwork.
Emotional Support through Nature
The natural environment provides numerous opportunities for children to explore and express emotions. Activities like nature walks, gardening, and observing wildlife allow children to connect with nature and experience peace and relaxation. This connection to nature supports emotional development by helping children manage stress, develop empathy, and build a sense of belonging and well-being.
Educators can create a balanced learning setting that supports children’s social and emotional development by thoughtfully designing outdoor learning environments with active play and quiet reflection. These environments provide children the tools and opportunities to build strong social relationships, manage their emotions effectively, and develop a deep connection to the natural world.


Practical Tips for Creating Effective Outdoor Learning Environments
Creating an effective outdoor environment requires thoughtful planning and a focus on safety and engagement. The layout should include different zones that cater to various activities, ensuring a balance between quiet and active areas. This allows children to experience a range of outdoor play activities that support their overall development. Designing the space with children’s interests in mind can make the outdoor environment more engaging and beneficial.
The selection of equipment is crucial for fostering a stimulating outdoor space. Choose tools and structures supporting physical, cognitive and social development. Equipment should be durable and suitable for different age groups to ensure it meets the needs of all children. Incorporating elements encouraging exploration and hands-on learning can significantly enhance the learning experience.
Elements that promote problem-solving abilities:
- Activity Panels: Panels with puzzles, games, and educational activities.
- Sensory Gardens: Gardens that engage children’s senses through touch, smell, and sight.
- Interactive Play Elements: Tools like water tables and loose parts for creative play.
- Organic Materials: Use wood, sand, and plants for sensory-rich environments.
- Quiet Zones: Areas for reflection and calm activities.
Incorporating loose parts into the play area can significantly further learning objectives and enhance creativity and problem-solving skills. Items such as stones, sticks, and leaves can be used in countless ways, sparking imagination and encouraging children to create games and scenarios. These open-ended materials provide endless learning opportunities and support cognitive development and fine motor skills.
Adapting the space to reflect the education of young children’s interests and developmental needs ensures that it remains engaging and relevant. Regularly updating the outdoor environment with new materials, themes, and activities can keep the space fresh and exciting. Observing how children interact with the environment and adjusting based on their feedback can help create a more dynamic and responsive learning area.
By integrating these elements into outdoor play environments, educators can create spaces that are not only fun and engaging but also educational and supportive of children’s holistic development. Whether through structured activities or free play, a well-designed outdoor play space can provide numerous opportunities for growth, exploration, and discovery.


Cultivating Lifelong Learning through Outdoor Play
Creating a vibrant and effective learning environment for play and learning is a powerful way to support children’s physical, cognitive, emotional, and social development. Educators can transform any outdoor space into a dynamic area where play and learning intertwine by integrating diverse outdoor activities and thoughtful design elements. These environments allow children to explore nature, engage in physical activity, and develop essential skills that will serve them throughout their lives.
The benefits of outdoor play extend far beyond the boundaries of traditional indoor spaces. Outdoor environments provide unique opportunities for children to develop gross motor skills, enhance cognitive abilities, and build strong social connections. Whether through structured preschool outdoor activities or free play at a local park, outdoor time is crucial for fostering a well-rounded development. Incorporating elements like activity panels, sensory gardens, and natural materials into learning environments can make these spaces even more enriching and engaging.
In addition to promoting physical health, outdoor activities play a significant role in children’s emotional and social development. The freedom and space provided by environments allow children to express themselves more freely, manage their emotions effectively, and develop resilience. Quiet zones, such as picnic tables or shaded areas, offer spaces for reflection and calm activities, balancing the more active areas and ensuring children experience full emotional growth.
As educators and parents continue to recognize the value of outdoor play, initiatives like the Natural Learning Initiative can provide valuable guidance and resources for creating these enriching environments. By observing how children interact with outdoor spaces and making thoughtful adjustments, we can ensure that these environments remain dynamic, engaging, and supportive of all aspects of children’s development. From toddlers to older children, learning environments offer countless opportunities for play, learning, and discovery, setting the foundation for a lifelong love of learning and exploration.